EN
Translate:
EN
EN
Translate:
EN
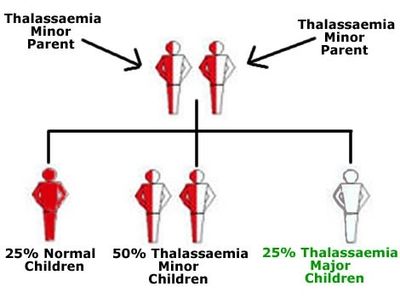
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder in which the body makes an abnormal form of haemoglobin.
Haemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. People with the condition produce either no or too little haemoglobin, which is used by red blood cells to carry oxygen around the body. The disorder results in excessive destruction of red blood cells.
There are different types of thalassaemia, which can be divided into alpha and beta thalassaemia. Beta thalassaemia major is the most severe type. Other types include beta thalassaemia intermedia, alpha thalassaemia major and haemoglobin H disease.
The symptoms of thalassemia can vary. The symptoms of thalassemia major generally appear before a child’s second birthday. The severe anaemia related to this condition can be life-threatening and requires regular blood transfusions.
Other signs and symptoms include:
Not everyone has visible symptoms of thalassemia. Signs of the disorder can also tend to show up later in childhood or adolescence
Thalassaemia trait or carrier means this does not normally cause problems and no symptoms can occur. It is extremely rare for it to cause problems or complications. If both parents are carriers, then there’s a 25% chance each child they have being born with the full condition. Blood tests can also be carried out at any age to check for the condition or to see if you're a carrier.
It is important to keep safe and well. Living with Thalassaemia Major will affect people in different ways but should not stop anyone from being active.
A few helpful tips include:

